Methylsalicylat Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
FARBLOSEODER GELBE BIS ROTE, ?LIGE FLüSSIGKEIT MIT CHARAKTERISTISCHEM GERUCH.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Reagiert mit starken Oxidationsmitteln und starken Basen.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt (ACGIH 2004). MAK nicht festgelegt (DFG 2004).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation, über die Haut und durch Verschlucken.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Nur ungenügende Angaben vorhanden über die Geschwindigkeit, mit der eine gesundheitssch?dliche Konzentration in der Luft beim Verdampfen bei 20°C erreicht wird.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Die Substanz reizt die Augen und die Haut. M?glich sind Auswirkungen auf das Zentralnervensystem mit nachfolgendem Schock und Tod. Die Auswirkungen treten u.U. verz?gert ein. ?rztliche Beobachtung notwendig.
LECKAGE
Ausgelaufene Flüssigkeit in abdichtbaren Beh?ltern sammeln. Reste mit Sand oder inertem Absorptionsmittel aufnehmen und an einen sicheren Ort bringen. NICHT in die Umwelt gelangen lassen.
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.
R36/38:Reizt die Augen und die Haut.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
S24/25:Berührung mit den Augen und der Haut vermeiden.
Beschreibung
Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic ester that is naturally produced by many species of plants. Some of the plants which produce it are called wintergreens, hence the common name. This compound is used as a fragrance. It is also found in liniments (rubbing ointments).
Chemische Eigenschaften
Methyl Salicylate is the main component of wintergreen oil and occurs in small quantities in other essential oils and fruits. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic wintergreen-like odor. May be prepared by extraction from natural sources; or by esterification of salicylic acid with methanol.
Occurrence
Numerous plants produce methyl salicylate in very small amounts. Some plants, such as the following, produce more:
Some species of the genus Gaultheria in the family Ericaceae, including Gaultheria procumbens, the wintergreen or eastern teaberry;
Some species of the genus Betula in the family Betulaceae, particularly those in the subgenus Betulenta such as B. lenta, the black birch;
All species of the genus Spiraea in the family Rosaceae, also called the meadowsweets.
This compound is produced most likely as an anti-herbivore defense. If the plant is infected with herbivorous insects, the release of methyl salicylate may function as an aid in the recruitment of beneficial insects to kill the herbivorous insects.Aside from its toxicity, methyl salicylate may also be used by plants as a pheromone to warn other plants of pathogens such as tobacco mosaic virus.
Verwenden
Methyl salicylate is an organic ester that is commonly produced naturally by wintergreens. Methyl salicylate is utilize as a anti-herbivore defense system in various plants that produces it. Methyl sa
licylate is also used in high concentrations as a rubefacient to treat joint, muscular pain and acute pain. Methyl slicylate is also used as a flavoring agent and often used to provide fragrance to pr
oducts.
Definition
ChEBI: Methyl salicylate is a benzoate ester that is the methyl ester of salicylic acid. It has a role as a flavouring agent, a metabolite and an insect attractant. It is a benzoate ester, a member of salicylates and a methyl ester. It is functionally related to a salicylic acid.
Vorbereitung Methode
Methyl acetate, a novel acyl acceptor for biodiesel production has been developed, and a comparative study on Novozym 435-catalyzed transesterification of soybean oil for biodiesel production with different acyl acceptors has been studied (Noureddini et al., 2005).
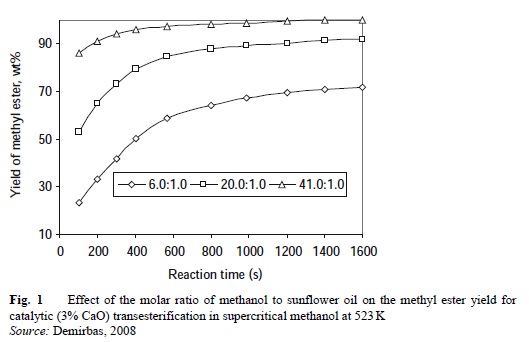
Figure 1 shows the effect of the molar ratio of methanol to sunflower oil on the methyl ester yield for catalytic (3% CaO) transesterification in supercritical methanol at 523 K.
synthetische
Methyl salicylate can be produced by esterifying salicylic acid with methanol. Commercial methyl salicylate is now synthesized, but in the past, it was commonly distilled from the twigs of Betula lenta (sweet birch) and Gaultheria procumbens (eastern teaberry or winter green).
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Colorless yellowish or reddish liquid with odor of wintergreen.
Air & Water Reaktionen
Insoluble in water.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
Methyl Salicylate is an ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Birch-Me is incompatible with oxidizers. Birch-Me is also incompatible with strong bases. Birch-Me may react with iron salts.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion; use in foods restrictedby FDA, lethal dose 30 cc in adults, 10 cc in chil-dren.
Health Hazard
Methyl salicylate is a highly toxic compound.The toxic symptoms in humans include nausea, vomiting, gastritis, diarrhea, respiratorystimulation, labored breathing, pulmonaryedema, convulsions, and coma. Ingestion of15 to 25 mL of this compound may befatal to humans. Application of the liquidon the skin and eyes produced severe irrita tion in rabbits. Oral, subcutaneous, or der mal administration of methyl salicylate intest animals produced specific developmen tal abnormalities affecting the eyes, ears, andcentral nervous system
Toxicity of this compound is relativelymore severe in humans than in many com mon laboratory animals. The oral LD50 values in test animals were within the range800–1300 mg/kg.
Brandgefahr
Methyl salicylate is combustible.
Kontakt-Allergie
This anti-inflammatory agent is found in a wide number of ointments and can induce allergic contact dermatitis.
Sicherheitsprofil
Human poison by
ingestion. Moderately toxic to humans by an
unspecified route. Moderately toxic
experimentally by intraperitoneal,
intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. An
experimental teratogen. Human systemic
effects by ingestion: flaccid paralysis without
anesthesia, general anesthesia, dyspnea,
nausea, vomiting, and respiratory
stimulation. Experimental reproductive
effects. A severe skin and eye irritant.
Ingestion of relatively small amounts has
caused severe poisoning and death.
Combustible liquid when exposed to heat or
flame; can react with oxibzing materials. To
fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. When
heated to decomposition it emits acrid
smoke and irritating fumes.
Sicherheit(Safety)
In pure form, methyl salicylate is toxic, especially when taken internally. A single teaspoon (5ml) of methyl salicylate contains 7g of salicylate, which is equivalent to more than twenty- three 300 mg aspirin tablets. The lowest published lethal dose is 101 mg / kg body weight in adult humans , (or 7.07 grams for a 70 - kg adult). It has proven fatal to small children in doses as small as 4 ml.[6] A seventeen-year- old cross - country runner at Notre Dame Academy on Staten Island, died in April 2007, after her body absorbed methyl salicylate through excessive use of topical muscle-pain relief products.
Most instances of human toxicity due to methyl salicylate are a result of over-application of topical analgesics, especially involving children. Some people have intentionally ingested large amounts of oil of wintergreen. Salicylate, the major metabolite of methyl salicylate, may be quantitated in blood, plasma or serum to confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in hospitalized patients or to assist in an autopsy.
Carcinogenicity
Available data suggest that
methyl salicylate is not carcinogenic.
l?uterung methode
Dilute the ester with Et2O, wash with saturated NaHCO3 (it may effervesce due to the presence of free acid), brine, dry MgSO4, filter, evaporate and distil it. Its solubility is 1g/1.5L of H2O. The benzoyl derivative has m 92o (b 270-280o/120mm), and the 3,5-dinitrobenzoate has m 107.5o, and the 3,5-dinitrocarbamoyl derivative has m 180-181o. [Hallas J Chem Soc 5770 1965, Beilstein 10 IV 143.]
Toxicity evaluation
Oral LD50 values (mg/kg) for mouse, rat and rabbit are 1110, 887 and 1300, respectively. Oral LD50 values for child and adult human (mg/kg) are 228 and 506, respectively. Topical methyl salicylate generally rarely causes systemic toxicity, but it can be absorbed by the skin leading to stimulation of the central nervous system respiratory center, disturbance of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, and disturbance of intracellular respiration. Severe poisoning can lead to acute lung injury, lethargy, coma, seizures, cerebral edema, and death. In the case of salicylate intoxication, treatment includes general supportive care, purification of the gastrointestinal tract with activated charcoal in the case of ingestion of salicylic acid, and monitoring of serum salicylic acid concentration. Bicarbonate infusion or hemodialysis can be used to enhance the elimination of salicylic acid.
Methylsalicylat Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

