|
|
| | taxiphyllin Basic information |
| Product Name: | taxiphyllin | | Synonyms: | (2R)-Taxiphyllin;(2R)-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile;taxiphyllin;(2R)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyacetonitrile;Benzeneacetonitrile, α-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-4-hydroxy-, (αR)-;(R)-4-hydroxymandelonitrileβ-D-glucoside | | CAS: | 21401-21-8 | | MF: | C14H17NO7 | | MW: | 311.29 | | EINECS: | | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 21401-21-8.mol | 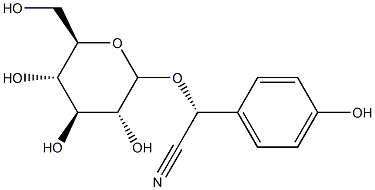 |
| | taxiphyllin Chemical Properties |
| | taxiphyllin Usage And Synthesis |
| Uses | Taxiphyllin (2R-Taxiphyllin) is a plant cyanogenic glycoside, which exhibits inhibitory activity for tyrosinase[2]. Taxiphyllin exhibits cytotoxicity in BRL-3A cellls with an IC50 of 18.75 μm[3] and antimicrobial activities against Staphylococcus aureus with an EC50 of 0.96 μM[4]. | | Definition | ChEBI: (R)-4-hydroxymandelonitrile beta-D-glucoside is a beta-D-glucoside consisting of (R)-prunasin carrying a hydroxy substituent at position 4 on the phenyl ring. It is a beta-D-glucoside and a nitrile. It is functionally related to a (R)-prunasin. | | References | [1] Yang CJ, et al. Two new cyanogenic glucosides from the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla. Molecules. 2012;17(5):5396-5403. DOI:10.3390/molecules17055396
[2] Wu B. Tyrosinase inhibitors from terrestrial and marine resources. Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14(12):1425-49. DOI:10.2174/1568026614666140523115357
[3] Yi JJ, et al., Characterisation and in vitro cytotoxicity of toxic and degradation compounds in bamboo shoots (Dendrocalamus Sinicus) during traditional fermentation. Int J of Food Sci Tech. 2020
[4] Oueslati MH, et al., Phytochemical constituents from Salsola tetrandra. J Nat Prod. 2006 Sep;69(9):1366-9. DOI:10.1021/np060222w |
| | taxiphyllin Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|