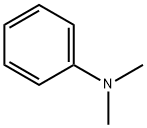
N,N-??????
|
|
N,N-?????? ??
- ???
- 1.5-2.5 °C (lit.)
- ?? ?
- 193-194 °C (lit.)
- ??
- 0.956 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
- ?? ??
- 3 (vs air)
- ???
- 2 mm Hg ( 25 °C)
- ???
- n
20/D 1.557(lit.)
- ???
- 158 °F
- ?? ??
- Store below +30°C.
- ???
- 1.2g/L
- ?? ?? (pKa)
- 5.15(at 25℃)
- ??? ??
- ??
- ??
- ?? ???
- ????
- 0.179
- ??????(pH)
- 7.4 (1.2g/l, H2O, 20℃)
- ????
- 1.2-7%(V)
- ???
- 1g/L(20℃)
- Merck
- 14,3234
- BRN
- 507140
- Henry's Law Constant
- 4.98(x 10-6 atm?m3/mol) at 20 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure)
- ?? ??
- NIOSH REL: TWA 5 ppm (25 mg/m3), STEL 10 ppm (50 mg/m3), IDLH 100 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 5 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 ppm, STEL 10 ppm (adopted).
- Dielectric constant
- 4.4000000000000004
- ???
- ????. ????, ??, ? ???, ? ???, ????????, ???? ???? ????. ?? ??.
- InChIKey
- JLTDJTHDQAWBAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- LogP
- 1.171 at 35℃
- CAS ??????
- 121-69-7(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 3 (Vol. 57) 1993
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | T,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 61-20/21-51/53-40-23/24/25 | ||
| ????? | 53-45-61-36/37-28A-28 | ||
| ????(UN No.) | UN 2253 6.1/PG 2 | ||
| OEB | A | ||
| OEL | TWA: 5 ppm (25 mg/m3), STEL: 10 ppm (50 mg/m3) [skin] | ||
| WGK ?? | 3 | ||
| RTECS ?? | BX4725000 | ||
| F ?????? | 8 | ||
| ?? ?? ?? | 370 °C DIN 51794 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS ?? | 2921 42 00 | ||
| ?? ?? | 6.1 | ||
| ???? | II | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 121-69-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| ?? | LD50 orally in rats: 1.41 ml/kg (Smyth) | ||
| IDLA | 100 ppm | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-05-0532 | ||
| ?????? ??? | 97-1-183 | ||
| ?? ? ???? | ????: ????; ???(??)????: ?? ??? ? ? ??? 25% ?? ??? ??? |
N,N-?????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??? ??
N,N-Dimethylaniline is a light yellow to light brown oily liquid. Has a pungent odor. Soluble in ethanol, chloroform, ether and aromatic organic solvents, slightly soluble in water.It is a tertiary amine used in the synthesis of several triarylmethane dyes like malachite green. It is also used in the synthesis of a magnetic gram stain for the detection of bacteria.??? ??
Straw to brown-colored oily liquid with a characteristic amine-like odor. Odor threshold concentration is 13 ppb (quoted, Amoore and Hautala, 1983).??
N,N-dimethylaniline is an important dye intermediate. It can be used to prepare alkaline yellow, Crystal Violet 5BN, basic magenta green, basic lake blue BB, basic brilliant blue R, cationic red 2BL, brilliant red 5GN, violet 3BL, brilliant blue, etc. In the pharmaceutical industry, the product can be used to manufacture cefazolin V, sulfamonomethoxine, Sulfadoxine, fluorocytosine, etc. moreover, It can be used as an intermediate to vanillin, a stabilizer for colorimetric peroxidase determination or as a reagent in chemical synthesis.??
ChEBI: N,N-dimethylaniline is a tertiary amine that is aniline in which the amino hydrogens are replaced by two methyl groups. It is a tertiary amine and a dimethylaniline.?? ??
N,N-Dimethylaniline is made by heating aniline, methyl alcohol and sulfuric acid under pressure, followed by hydrolysis of the sulfate formed with sodium hydroxide to the free base (Windholz et al 1983). United States production in 1975 was estimated at 4,600 metric tons (HSDB 1989).?? ??
N,N-Dimethylaniline appears as a yellow to brown colored oily liquid with a fishlike odor. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Flash point 150°F. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption. Used to make dyes and as a solvent.??? ?? ??
Insoluble in water.?? ???
Explosive decomposition occurred when finely divided benzoyl peroxide was allowed to react with N,N-Dimethylaniline by breaking an ampoule containing 0.5 grams of dimethylaniline in an autoclave, NFPA 491M, 1991. This result may be expected with other peroxides and various oxidants.????
Clinical signs of intoxication with N,N-dimethylaniline in man are headaches, cyanosis, dizziness, labored breathing, paralysis and convulsions (HSDB 1989). It is absorbed through the skin to produce a dangerous methemoglobinemia (Gosselin 1984). Treatment is similar to that of aniline with the object of managing methemoglobinemia.????
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.?? ??
N,N-Dimethylaniline is used as chemical intermediate in the manufacturing of vanillin, Michler's ketone, and dyes such as Acid Red 2, Basic Green 4 and Basic Violet 1 (Northcott 1978). It is also used as a solvent and an activator for polyesters and as an alkylating agent (Beard and Noe 1981). It is used as an acid scavenger or accepter in the manufacture of beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillin and cephalosporin (Nachtmann and Gstrein 1981).Safety Profile
Suspected carcinogen with equivocal tumorigenic data. Human poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by inhalation and skin contact. A skin irritant. Human systemic effects by ingestion: nausea or vomiting. Physiological action is similar to, but less toxic than, adne. A central nervous system depressant. Mutation data reported. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. Explodes on contact with benzoyl peroxide or disopropyl peroxydicarbonate. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits htghly toxic fumes of adne and NOx. See also ANILINE.Carcinogenicity
A 2-year corn oil gavage bioassay conducted by NTP in F344/N rats (0.3 or 30 mg/kg) and B6C3F1 mice (0, 15, or 30 mg/kg) for 103 weeks concluded that there was some evidence of carcinogenic activity for male F344/N rats as indicated by the increased incidences of sarcomas or osteosarcomas in the spleen; there was no evidence of carcinogenic activity in the female rats or male mice; there was equivocal evidence of carcinogenic activity for female mice as indicated by an increased incidence of squamous cell papillomas of the forestomach. Both rats and mice could have tolerated doses higher than those used in these studies.????
Photolytic. A rate constant of 1.48 x 10-10 cm3/molecule?sec was reported for the reaction of N,N-dimethylaniline and OH radicals in air at room temperature (Atkinson et al., 1987).Chemical/Physical. Products identified from the gas-phase reaction of ozone with N,Ndimethylaniline in synthetic air at 23 °C were: N-methylformanilide, formaldehyde, formic acid, hydrogen peroxide, and a nitrated salt having the formula: [C6H6NH(CH3)2]+NO3 - (Atkinson et al., 1987). Reacts with acids forming water-soluble salts.
?? ??
Ν,Ν-Dimethylaniline undergoes N-demethylation, N-oxidation, and ring hydroxylation in animals. Urinary metabolites produced by dogs and rabbits injected with this compound included 4-aminophenol, 4-dimethylaminophenol, 2-aminophenol and N-methylaniline (Williams 1959; Kiese and Renner 1974). N-oxidation, N-demethylation and ring hydroxylation of Ν,Ν-dimethylaniline was demonstrated in vitro using liver microsomal preparations from pigs, rats, rabbits, chickens, and guinea pigs (Fish et al 1955; Zeigler and Pettit 1964, 1966; Abou-Donia and Menzel 1968). N-oxidation was also demonstrated using whole homogenate of human liver (Zeigler and Gold 1971; Rane 1974). Evidence has been obtained with rabbit liver microsomes for two pathways for Ν,Ν-dimethylaniline N-oxidation (Hlavica and Kehl 1977). One pathway involves cytochrome P-450 while the second makes use of flavin-containing monooxygenase. N,N-Dimethylaniline was also metabolized to formaldehyde in the nasal and respiratory mucosa of Fischer 344 rats (McNulty et al 1983). Alveolar type II cells from rabbit and rat lungs catalyzed the N-oxidation of this compound (Devereux and Fouts 1974; Ohmiya and Mehendale 1981). The microsomal preparation from rat seminal vesicles when fortified with arachidonic acid catalyzed the dealkylation of N,Ndimethylaniline (Sivarajah et al 1982).?? ??
N,N-Dimethylaniline and 1-(trifluoromethyl)benzene-functionalized tetrakis(ethynyl)pyrenes: synthesis, photophysical, electrochemical and computational studies DOI:10.1016/J.TET.2011.12.066Friedel-Crafts Reaction of N,N-Dimethylaniline with Alkenes Catalyzed by Cyclic Diaminocarbene-Gold(I) Complex doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29854-0
Groundwater Chemicals Desk Reference DOI:10.5860/choice.27-6127
Patty's Toxicology 6-Volume Set-Wiley (2012)
Proctor Proctor and Hughes' chemical hazards of the workplace (5th edn) Wiley Interscience DOI:10.1002/JAT.1034
Nitrogen and phosphorus solvents DOI:10.1016/c2009-0-01359-2
Purification of Laboratory Chemicals DOI:10.5860/choice.50-6768
N,N-?????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??
4-CHLORO-2-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PYRIMIDINE
6-????????
6-N-???????
?? ??
???
2-Amino-4-ethylpyridine
4, 4^<'^>-dimethylamino diphenyl ketone
C.I. ? ???? 17, ??? ?
2,4-??????????
4-CHLORO-2,6-BIS(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PYRIMIDINE
2,4-Dichloro-5-fluoropyrimidine
?????
???? ?? B
Magentagreencrystals
2,4-DIMETHOXYPYRIMIDINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID
5-Bromo-4,6-dichloropyrimidine
?? ??? 8
6-N-???????
Basic Dyestuff
4-Bromo-N,N-dimethylaniline
6-?????
4,4'-?????(N,N-???)????
6-CYANOPURINE
N,N-DIMETHYL-3-NITROANILINE
N,N,N',N'-????????
??? ?? B
6-benzylaminopurine
Mifepristone
7-METHYLGUANINE
6-????????
Basic Blue 53
Basic Red 22
??????
leucotrope O
2-???-3,5-????-4,6-??????
N,N-DIMETHYL-M-PHENYLENEDIAMINE
2,4-DICHLORO-6-FLUOROPYRIMIDINE
6-N-?????
Phenmedipham
6-?????
N,N-?????? ?? ??
???( 606)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shandong Zhishang New Material Co., Ltd. | +8617653113209 |
sales002@sdzschem.com | China | 3049 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418684 +8618949823763 |
sales@tnjchem.com | China | 25356 | 58 |
| Lihe Pharm Technology(Wuhan)Co.,Ltd | +8618071517867 |
info@lihepharma.com | China | 192 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 |
abby@weibangbio.com | China | 8810 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12835 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5889 | 58 |
| Capot Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-(0)57185586718 +86-13336195806 |
sales@capot.com | China | 29791 | 60 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21634 | 55 |
| Anhui Royal Chemical Co., Ltd. | +86-25-86655873 +8613962173137 |
marketing@royal-chem.com | China | 193 | 55 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418679 +8618949832763 |
info@tnjchem.com | China | 2986 | 55 |