5959-95-5
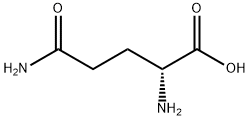 5959-95-5 結(jié)構(gòu)式
5959-95-5 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
D-氨羰基丁氨酸
D-麩氨酰胺
D-谷氨酸酰胺
D(-)-GLUTAMIC ACID-5-AMIDE
D-GLUTAMIC ACID 5-AMIDE
D(-)-GLUTAMINE
D-GLUTAMINE
D-GLUTAMINIC ACID 5-AMIDE
H-D-GLN-OH
(R)-2-AMINO-4-CARBAMOYL-BUTYRIC ACID
(2R)-2-amino-4-carbamoyl-butanoic acid
D-Glutamine (9CI)
Glutamine,D-(8Cl)
D-Gln-OH
D-GLUTAMINE extrapure
D-2-Aminoglutaramic acid, D-Glutamic acid 5-amide
Citric Acid, Monohydrate, Crystal, Reagent
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
安全數(shù)據(jù)
知名試劑公司產(chǎn)品信息
D(-)-Glutamine, 98%(5959-95-5)
D-Glutamine,>98.0%(T)(5959-95-5)
| 報價日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號 | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號 | 包裝 | 價格 |
| 2024/11/11 | XW59599553 | D-谷氨酰胺 d-glutamine;2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid;2-aminoglutaramic acid;glutamic acid 5-amide;h-d-gln-oh | 5959-95-5 | 25G | 582元 |
| 2024/11/11 | XW59599551 | D-谷氨酰胺 d-glutamine;2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid;2-aminoglutaramic acid;glutamic acid 5-amide;h-d-gln-oh | 5959-95-5 | 1G | 54元 |
| 2024/11/08 | 13516 | D-谷氨酰胺 D(-)-Glutamine, 98% | 5959-95-5 | 1g | 1119元 |
常見問題列表
|
Human Endogenous Metabolite
|
Glutamine is a key amino acid in the central nervous system (CNS), playing an important role in the glutamate/GABA-Glutamine cycle (GGC). In the GGC,Glutamine is transferred from astrocytes to neurons, where it will replenish the inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitter pools. D-Glutamine has been used to study its role in conferring protection against acetaldehyde-induced disruption of barrier function in Caco-2 cell monolayer. Role of L-Glutamine in the protection of intestinal epithelium from acetaldehyde-induced disruption of barrier function is evaluated in Caco-2 cell monolayer. L-Glutamine reduced the acetaldehyde-induced decrease in transepithelilal electrical resistance and increase in permeability to inulin and lipopolysaccharide in a time- and dose-dependent manner; D-Glutamine, L-aspargine, L-arginine, L-lysine, or L-alanine produced no significant protection. D-Glutamine also fails to influence the acetaldehyde-induced decrease in TER and increase in inulin flux. D-Glutamine or glutaminase inhibitor by themselves did not influence TER or inulin flux in control or acetaldehyde-treated cell monolayers. Lack of effect of D-Glutamine in protection from acetaldehyde indicates that the L-Glutamine-mediated protection is stereospecific.
