| Identification | More | [Name]
Borane-tetrahydrofuran complex | [CAS]
14044-65-6 | [Synonyms]
BORANE
BORANE-TETRAHYDROFURAN
BORANE TETRAHYDROFURAN COMPLEX
BORON HYDRIDE-TETRAHYDROFURAN COMPLEX
TETRAHYDROFURAN BORANE
borane-tetrahydrofurancomplex,bthf-1m
borane-tetrahydrofurancomplex,bthf-2m
Borane tetrahydrofuran complex solution
Borane-tetrahydrofuran complex, 1M solution tetrahydrofuran
Borane-tetrahydrofuran complex, 2M solution tetrahydrofuran
BORANE-TETRAHYDROFURAN COMPLEX, CA. 1.8M SOLUTION IN TETRAHYDROFURAN, TECH.
BORANE-TETRAHYDROFURAN COMPLEX 1.0M SO&
BORANE-TETRAHYDROFURAN COMPLEX, 1.0M SOLUTION IN TETRAHYDROFURAN
BORANE-TETRAHYDROFURAN COMPLEX, 1.5M SOL N IN TETRAHYDROFURAN AND ETHER, TECH.
BORANE TETRAHYDROFURAN COMPLEX SOLUTION, 4X10 ML
BORANE TETRAHYDROFURAN COMPLEX SOLUTION, ~1 M IN THF
Borane-tetrahydrofuran complex, 1M solution in THF, stabilized
Borane,tetrahydrofurancomplex,1MinTHF
Boron, trihydro(tetrahydrofuran)-, (T-4)-
borane tetrahydrofuran complex, 1m soln. in thf | [EINECS(EC#)]
237-881-8 | [Molecular Formula]
C4H11BO | [MDL Number]
MFCD00012429 | [Molecular Weight]
85.94 | [MOL File]
14044-65-6.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
colourless liquid | [Melting point ]
-17 °C | [Boiling point ]
35 °C | [density ]
0.898 g/mL at 25 °C
| [Fp ]
1 °F
| [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [form ]
Liquid | [color ]
Colorless | [Stability:]
Stable, but may form explosive peroxides in contact with air. Incompatible with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, oxidizing agents, alcohols. Reacts violently with water. Highly flammable. Store under inert gas. | [Water Solubility ]
REACTS | [Sensitive ]
Air & Moisture Sensitive | [BRN ]
3668402 | [CAS DataBase Reference]
14044-65-6(CAS DataBase Reference) | [Storage Precautions]
Store under nitrogen | [EPA Substance Registry System]
14044-65-6(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
F,Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R14/15:Reacts violently with water, liberating extremely flammable gases .
R19:May form explosive peroxides.
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin .
R41:Risk of serious damage to eyes.
R37/38:Irritating to respiratory system and skin .
R11:Highly Flammable.
R67:Vapors may cause drowsiness and dizziness.
R66:Repeated exposure may cause skin dryness or cracking. | [Safety Statements ]
S16:Keep away from sources of ignition-No smoking .
S33:Take precautionary measures against static discharges .
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection .
S7/9:Keep container tightly closed and in a well-ventilated place .
S7/8:Keep container tightly closed and dry .
S43:In case of fire, use ... (indicate in the space the precise type of fire-fighting equipment. If water increases the risk add-Never use water) .
S37/39:Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection .
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing .
S29:Do not empty into drains . | [RIDADR ]
UN 3399 4.3/PG 1
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [F ]
1-10-13-34 | [TSCA ]
Yes | [HazardClass ]
4.3 | [PackingGroup ]
I | [HS Code ]
29321900 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Borane tetrahydrofuran complex (BH3-THF) is widely used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis. It is also used as a reagent in hydroboration reactions.It is a charge-transfer complex that is a useful surrogate for diborane1 in organic synthesis. It can be used to reduce carboxylic acids to alcohols or nitriles to primary amines. It reacts with olefins to add the BH2 functional group. Alkyl- or arylboranes formed in this way can further react with unsaturated compounds such as olefins, imines, ketones, and alkynes (the hydroboration reaction) to make useful boron-containing intermediates. | [Chemical Properties]
colourless liquid | [Uses]
Borane-tetrahydrofuran complex is used to reduce Nylon surface amide groups to secondary amines.
| [Application]
New, Safer, NIMBA-Stabilized BH3 THF Solutions
BH3-THF can be used as a reducing agent for the reduction of various functional groups such as carboxylic acids, aldehydes, ketones, esters, acid chlorides, nitriles, epoxides, amides, lactones, oximes, and imines into corresponding alcohols and amines. Grignard reagents, arylmercury, arylthalium, and allyl and propargyllithium compounds react with BH3?THF to give organoboranes, which can be oxidized to the corresponding alcohols, phenols, and 1,3-diols.
It can also be used:
To synthesize the chiral borane catalyst, which is used in the enantioselective halo-aldol reaction.
To prepare 9-unsubstituted acridines by reduction of corresponding acridones.
To reduce nylon surface amide groups to secondary amines. | [Reactions]
Borane-tetrahydrofuran complex (BTHF) is a valuable reagent for the reduction of functional groups and for hydroboration reactions with carbon-carbon double and triple bonds. Functional groups that are readily reduced by BTHF include aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, amide, oxime, imine, and nitrile. The carboxylic acid group is reduced at a faster rate than most groups including non-conjugated alkene. Conjugated α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids give saturated alcohols as the major products.
Ketones and the carbonyl of enones are effectively reduced with borane-tetrahydrofuran. The addition of borohydride to the reaction solution is advantageous for accelerated reduction as well as higher selectivity towards carbonyl reduction in conjugated and non-conjugated enones.
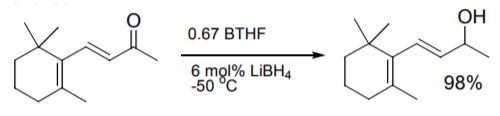
Asymmetric ketone reduction using chiral oxazaborolidine catalysts was recently reviewed. Work at Callery with BTHF improved on reaction conditions to provide consistent results in the reduction. | [General Description]
Borane tetrahydrofuran complex (BH3-THF) is widely used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis. It is also used as a reagent in hydroboration reactions. | [Precautions]
Air and moisture sensitive. Forms explosive peroxides in contact with air. Incompatible with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, oxidizing agents and alcohols. On hydrolysis, it forms hydrogen and boric acid. |
|
|