| Identification | More | [Name]
Alendronate sodium | [CAS]
129318-43-0 | [Synonyms]
4-AMINO-1-HYDROXY-1-PHOSPHONOBUTYL PHOSPHONIC ACID, MONOSODIUM
4-amino-1-hydroxybutylidene-1,1-bisphosphonic acid monosodium salt
ALENDRONATE
ALENDRONATE SODIUM
alendronic acid monosodium salt
alendros
bifosa
fosalan
FOSAMAX
MK-217
monosodium alendronate
neobon
osteovan
SODIUM ALENDRONATE
(4-Amino-1-hydroxybutylidene) bisphosphonic acid monosodium salt
Alendronate sodium
Fosamax
Sodium 4-amino-1-hydroxy-1-phosphonobutane-1-phosphonate | [EINECS(EC#)]
603-329-3 | [Molecular Formula]
C4H13NNaO7P2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD01861681 | [Molecular Weight]
272.09 | [MOL File]
129318-43-0.mol |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [HazardClass ]
IRRITANT | [Toxicity]
dog,LD,oral,> 200mg/kg (200mg/kg),International Journal of Clinical Practice, Supplement. Vol. 101, Pg. 3, 1999. |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Overview]
Alendronate sodium is the world's most widely used anti-osteoporosis drugs, listed in the United States in 1993. It can significantly increase bone mineral density, reduce fracture risk, and it is the first-line treatment of osteoporosis drugs. Alendronate sodium is a resorption inhibitor of aminodiphosphonate bone, and has a strong affinity with bone hydroxyapatite. It can enter the bone matrix hydroxyapatite crystals. When the osteoclast dissolved crystals, the drug was released, causing the inhibition of osteoclast activity, and playing anti-bone resorption activity indirectly through the inhibition of bone resorption of osteoblasts.
It possesses the characteristics of the activity of anti-bone resorption and with no bone mineralization. Clinically used for the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, to prevent hip and spine fractures. It is important to note that calcium and vitamin D supplements should be administered to all patients with osteoporosis, if they are unable to ingest enough calcium and vitamin D from their diet.
Osteoporosis is a disease that leads to an increased risk of fracture. It is characterized by a reduction in bone mineral density, a deterioration of bone microstructure, and changes in the amount and type of proteins within the bones. The main risk of osteoporosis is caused by increased risk of fracture in patients which is rarely happened in healthy human beings. This fracture is also known as fragile fractures. The common parts includes the spine, ribs, buttocks, wrist, etc., It is the main reason to the disability or death of the people with osteoporosis. Statistics show that the incidence of osteoporosis in the world is on the rise. The osteoporosis patients in the world have more than 200 million and the osteoporosis patients in China have about 70 million. Osteoporosis has become a key disease leading to a serious health hazard to human health, especially in middle-aged and elderly women. Bisphosphonates are a generic class of prescription drugs for the treatment of osteoporosis, including etidronate, Alendronate sodium, risedronate, zoledronic acid, etc. Their chemical share similar structure and pharmacological effects.
Alendronate sodium, trade name Fosamax, is the world's most widely used anti-osteoporosis drugs. The product is the third generation of amino diphosphonate bone resorption inhibitors, and has a strong affinity with bone hydroxyapatite, playing anti-bone resorption role by inhibiting osteoclast activity. Its anti-bone resorption is 1000 times stronger than that of etidronate, and there is no bone mineralization inhibition. Mainly used for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, it can increase the bone mass of the spine, vertebral body distortion, height reduction, fracture incidence (including the hip, spine, carpal) and so on. | [Synthesis of Alendronate]
It uses gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), phosphorous acid, phosphorus trichloride as the raw material and uses the diphenyl ether as the solvent to prepare the alendronic acid, and then alkalesizes to obtain its monosodium salt. The synthesis is shown below:
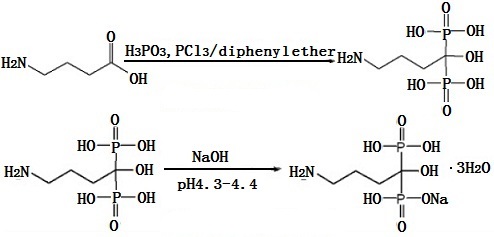
Image 1: Synthesis of Alendronate sodium | [Side effects]
After medication tolerance well, a small number of patients can be seen gastrointestinal reactions, such as nausea, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, occasional headache, skeletal muscle pain, rare rash and erythema.
The overview of Alendronate sodium, synthesis, adverse reactions, precautions, etc. is edited by Chemicalbook's Li Jie. (2016-01-22) | [Taboo]
1.Esophageal motility disorders, such as the disability of esophageal delay and the esophageal stricture are disabled.
2.Severe renal insufficiency is disabled.
3.Osteomalacia is disabled.
4.Allergies with the goods and other bisphosphonates, hypokalemia are disabled.
5.Pregnant, lactating women and children are disabled. | [Note]
1. At least 30 minutes before breakfast with 200ml warm water delivery; medication at least 30 minutes before eating.
2. Taking with orange juice and coffee at the same time will significantly affect the absorption of the product.
3. In taking this product before and after 30 minutes, drinking milk, dairy products and drinks with more calcium are not allowed. Immediately lying in bed after taking medicine may cause esophageal irritation or ulcerative esophagitis.
4. Gastrointestinal disorders, gastritis, esophageal discomfort, duodenitis, ulcer patients should use this drug with caution.
5, Mild to moderate renal dysfunction in patients should use this drug with caution.
6. Before starting to use this product treatment, calcium metabolism and mineral metabolism disorders, vitamin D deficiency and hypocalcemia must be corrected. Calcium supplements, antacids and some oral agents are likely to hinder the absorption of the product. Therefore, after taking this product, the time should be delayed at least half an hour and then taking other drugs.
7. If the food intake is not enough, all patients with osteoporosis should be added calcium and vitamin D. | [Drug interactions]
1. Antacids and cathartic agents will often affect the absorption of the drug for containing calcium or other metal ions such as magnesium, iron and so on.
2. Inducing hypocalcemia when in combination with aminoglycosides. |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Alendronate sodium is the fourth bisphosphonate to reach the market for the treatment
of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates are potent inhibitors of bone resorption.
They reduce pain and complications due to bone metastases, are effective in Paget's disease
and in increasing bone mineral density. These agents bind tightly to hydroxyapatite crystals
and are retained on bone resorption surfaces. Local release of the bisphosphonates occurs
by acidification during the process of the bone resorption to impair the osteoclasts' ability to
resorb bone. Alendronate is more potent than other bisphosphonates such as clodronate,
pamidronate, and etidronate and is reported to have no deleterious effects on bone. It has
also been shown to reduce hypercalcemia in cancer patients. | [Originator]
Istituto Gentili (Italy) | [Manufacturing Process]
4-Amino-1-hydroxybutylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (ABDT).
Orthosphophorous acid (102.7 g; 1.25 moles) is introduced into a 2 liter-flask
with condenser, stirrer and dropping funnel, placed on a thermostatized bath;
the air is then removed with a nitrogen stream which is continued during all
the reaction. The acid is melted by heating the bath to 95°C. When melting is
complete, 4-aminobutyric acid (103.3; 1 mole) is added under stirring which
is continued till obtaining a doughy fluid. Phosphorous trihalide (176 ml; 2
moles) is added dropwise causing the mixture to boil and evolution of gaseous
hydrochloric acid which is damped by means of a suitable trap. The addition
rate is adjusted so as to keep a constant reflux for about 60 minutes. When
the addition is nearly over, the mixture swells, slowly hardening. Stirring is
continued as long as possible, whereafter the mixture is heated for further 3
hours. Without cooling, but removing the bath, water (300 ml) is added, first
slowly and then quickly. Heating and stirring are started again. Decolorizing
charcoal is added and the mixture is boiled for about 5 minutes, then hotfiltered
on paper and the filtrate is refluxed for 6 hours. After cooling is slowly
poured in stirred methanol (1500 ml) causing thereby the separation of a
white solid which collected and dried (161 g; 64.6%). The structure of ABDT
is confirmed by IR spectrum, proton magnetic and nuclear magnetic
resonance spectrum and elemental analysis.
The sodium salt of this acid may be prepared by adding of equivalent of
sodium hydroxide. | [Brand name]
Alendros | [Therapeutic Function]
Antiosteoporotic | [Pharmacokinetics]
The second-generation agent alendronate sodium was the first bisphosphonate agent approved by the U.S.
FDA for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and Paget's disease of the bone and is 1,000-fold
more potent than etidronate. This derivative, when dosed continuously (5–10 mg/day for osteoporosis and 40
mg/day for Paget's disease) and given with oral calcium supplements (500 mg/day), produced well-mineralized
bone and significantly improved BMD (7% in the spine and 4% in the hip) within 18 months. In addition, the
vertebral fracture rate was shown to decrease by 47%. A side effect associated with alendronate, chemical
esophagitis, has been attributed to inadequate intake of water and lying down after taking the
medication. Specific patient instructions were developed to limit the incidence of upper gastrointestinal
problems and include: 1) taking the medication with 6 to 8 ounces of water on arising in the morning, 2)remaining in an upright position for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication, and 3) delaying drinking
other liquids/eating for at least 30 minutes, if not 1 to 2 hours, to allow maximal absorption of the agent. To
enhance absorption, calcium supplements and any aluminum- or magnesium-containing antacids should be
dosed separately from the agents in this class. | [Clinical Use]
The second-generation agent alendronate sodium was the first bisphosphonate agent approved by the U.S.
FDA for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and Paget's disease of the bone and is 1,000-fold
more potent than etidronate. |
|
|