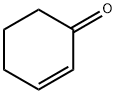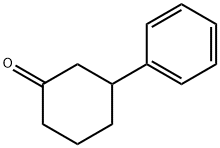
3-PHENYL-CYCLOHEXANONE synthesis
- Product Name:3-PHENYL-CYCLOHEXANONE
- CAS Number:20795-53-3
- Molecular formula:C12H14O
- Molecular Weight:174.24
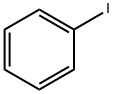
591-50-4
503 suppliers
$10.00/1g
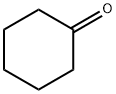
108-94-1
578 suppliers
$12.00/50g
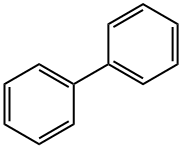
92-52-4
423 suppliers
$9.00/5g

20795-53-3
68 suppliers
$88.00/50mg
Yield:20795-53-3 76% ,92-52-4 10%
Reaction Conditions:
with palladium(II) trifluoroacetate;silver trifluoroacetate;tris(1-methylethyl)phosphine in 1,4-dioxane at 80; for 12 h;Catalytic behavior;Sealed tube;Inert atmosphere;Reagent/catalyst;Solvent;
Steps:
1 General Procedure for the β-Arylation of Ketones
General procedure: An 8 mL vial was charged with Pd(TFA)2 (10 mol %), AgTFA (2.0 equiv.), hexafluoroisopropanol (1 mL), ketone (2.5 equiv.) and aryl or heteroaryl iodide/bromide/tosylate/triflate (0.4 mmol). The vial was sealed with a PTFE lined cap and transferred to a glove box. The vial was opened and 1,4-dioxane (1 mL) and P(i-Pr)3 (20 mol %) were added under N2 purging. The vial was then sealed again and heated in a pie-block at 80° C. for 12 hours under stirring. After cooled to room temperature, the mixture was filtered through a small plug of silica gel and eluted with diethyl ether. The solvent was then removed under vacuum and flash column chromatography (hexane/ethyl acetate or DCM/methanol) of the residue gave the β-arylation product. Example 1 (0117) To demonstrate the feasibility of the disclosed methods, cyclohexanone (1a) and iodobenzene (2a) were used as the model substrates. A variety of palladium pre-catalysts, ligands, solvents and additives were examined (Table 1). Ultimately, It was discovered that use of palladium trifluoroacetate/triisopropyl phosphine as the pre-catalyst/ligand and silver trifluoroacetate as the promoter in 1,4-dioxane/hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) as mixed-solvents afforded the desired β-arylation product (3-phenyl cyclohexanone, 3a) in a 76% yield, along with 10% of biphenyl formed through the dimerization of iodobenzene (Eq. 1). Surprisingly, neither over-oxidation to 3-phenyl-cyclohexenone nor the α-arylation product was observed. The combination of electron-rich phosphine-Pd complexes and aryl or heteroaryl halides has been extensively employed in the ketone α-arylation reactions; however, while a similar combination is employed in the disclosed methods, this reaction proceeded with complete site-selectivity for the β-position. While not wishing to be bound by theory, this selectivity is believed to be explained by the fact that the Buchwald-Hartwig-Miura arylation typically uses stoichiometric bases to generate the corresponding enolates, but the disclosed methods operate under acidic conditions, which triggered a different activation mode (FIG. 1c).
References:
Board of Regents, The University of Texas System;Dong, Guangbin;Huang, Zhongxing US2016/229778, 2016, A1 Location in patent:Paragraph 0117
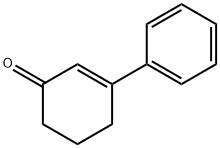
10345-87-6
36 suppliers
$317.00/1g

20795-53-3
68 suppliers
$88.00/50mg

108-94-1
578 suppliers
$12.00/50g
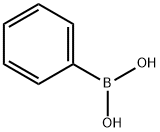
98-80-6
743 suppliers
$5.00/5g

20795-53-3
68 suppliers
$88.00/50mg