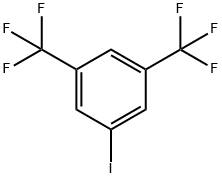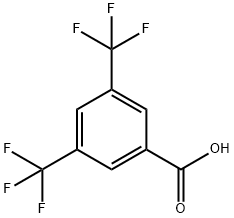
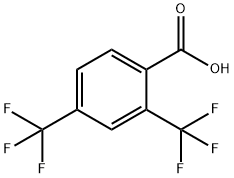
3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid synthesis
- Product Name:3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid
- CAS Number:725-89-3
- Molecular formula:C9H4F6O2
- Molecular Weight:258.12
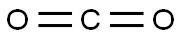
124-38-9
132 suppliers
$175.00/23402
328-70-1
438 suppliers
$10.00/25 g

725-89-3
335 suppliers
$10.00/5 g
Yield:725-89-3 90.3%
Reaction Conditions:
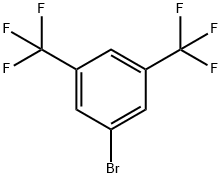
Stage #1:3,6-bis(trifluoromethyl)bromobenzene with n-butyllithium in tetrahydrofuran;hexane at -78; for 1 h;Inert atmosphere;
Stage #2:carbon dioxide in tetrahydrofuran;hexane at -78 - 20;
Steps:
4-Fluoro-2,6-dimethylbenzoic Acid (1); Typical Procedure
General procedure: Under a positive pressure of N2, 2-bromo-5-fluoro-1,3-dimethylbenzene(3.040 g, 1.0 equiv, 14.97 mmol) was added to aflame-dried 100 mL round-bottomed flask and then dilutedwith anhyd THF (20 mL). The solution was cooled to -78 °C anda 1.6 M solution of n-BuLi (1.055 g, 1.1 equiv, 16.47 mmol) inhexanes (10.29 mL) was added dropwise. The resulting solutionwas then stirred at -78 °C for 1 h.Separately, under a constant stream of N2, anhyd THF (~50 mL)was added to a flame-dried, 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask andcooled to -78 °C. Freshly milled dry ice (~75 g) was slowly addedto the flask from a powder funnel. The flask was vigorouslyswirled, ensuring that the milled dry ice remained completelysubmerged in the solvent. The resulting slurry was filtered byvacuum filtration under a constant stream of N2. After completeremoval of the solvent, the resulting milled dry ice was quicklytransferred to the original round-bottomed reaction flask byusing a powder funnel (see the Supporting Information foradditional details).The resulting reaction mixture was removed from the coolingbath and stirred at r.t. until complete sublimation of the dry icewas observed. (Safety Note: Sublimation of dry ice produces alarge amount of gas. To prevent a dangerous buildup of pressure,the reaction flask was left open to the atmosphere afterdry ice addition.) The solution was then concentrated in vacuo,and the residue was dissolved in H2O (25 mL) and CH2Cl2 (25mL). The resulting bilayer mixture was transferred to a separatoryfunnel, and the organic layer was removed. The aqueouslayer was washed with CH2Cl2 (3 × 25 mL) and acidified to pH 2-3 with 1 M aq HCl. The resulting aqueous solution was thenextracted with CH2Cl2 (4 × 25 mL), and the organic layers werecollected, dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated in vacuo togive a white solid; yield: 2.409 g (14.32 mmol, 95.68%, n = 4).
References:
O'Brien, Connor J.;Nicewicz, David A. [Synlett,2021,vol. 32,# 8,art. no. ST-2020-R0633-L,p. 814 - 816] Location in patent:supporting information
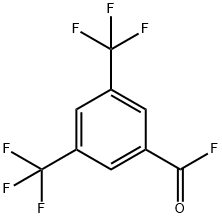
401-96-7
1 suppliers
inquiry

725-89-3
335 suppliers
$10.00/5 g
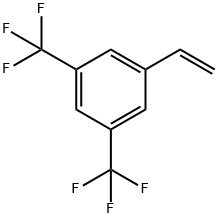
349-59-7
89 suppliers
$35.00/1g

725-89-3
335 suppliers
$10.00/5 g
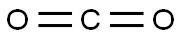
124-38-9
132 suppliers
$175.00/23402
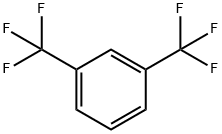
402-31-3
369 suppliers
$6.00/25g
32890-87-2
125 suppliers
$15.00/1g

725-89-3
335 suppliers
$10.00/5 g