What are the effects of Bisphenol A and its alternatives on human health?
Dec 16,2024
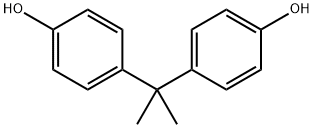
What is Bisphenol A?
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a synthetic oestrogen that is used extensively in the global plastics industry in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. BPA is found in many household products including food packaging, beverage containers, inks, textiles, emulsions, toys, electronic equipment, body coatings, medical devices, plastic PVC flooring and plumbing. However, these products are closely related to our lives and can be easily exposed through our diet, which can have a significant impact on our health.
Bisphenol A and its alternatives
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an endocrine disruptor that affects the growth, development and physiology of living organisms.BPA has been shown to leach into food and water, causing many negative health effects. As a result, it has been restricted and banned from use in many consumer products. Instead, many compounds with chemical structures similar to BPA have been used as alternatives to BPA in consumer products. Examples include bisphenol S (BPS), bisphenol F (4,4′-BPF), bisphenol AF (BPAF), bisphenol AP, bisphenol B, bisphenol C, bisphenol F, bisphenol G, bisphenol FL, and tetrabromo BPA.
Bisphenol S is the most studied of the bisphenol analogues and is the most common substitute for BPA. The reason for using BPS instead of BPA is that BPS is less likely to leach monomers into food and beverages. This is because BPS is generally more heat and light resistant than BPA.
Health Hazards
The hazards of Bisphenol A to humans are well known. However, as research has progressed it has been found that its substitutes do not appear to be safe either. Early studies have reported that early childhood exposure to endocrine disruptors such as bisphenols (BPs) (e.g., Bisphenol A, Bisphenol S, and Bisphenol F) may lead to obesity. Dietary intake of BPA substitutes known as Bisphenol S or BPS may be even more toxic and appears to lead to more lesions in the reproductive system. Bisphenol S has the same effects on obesity and metabolic disorders as all other bisphenols. However, dietary intake of BPS may induce certain types of breast cancer, cause DNA damage or weaken the immune system.
In vitro studies have shown that BPA and its analogues also affect oxidative stress and cellular energy metabolism in the female reproductive system, with BPA and BPF significantly decreasing the viability of KGN cells, whereas BPS and BPF showed mild toxic effects on the cells. Intracellular ROS production and antioxidant capacity of KGN cells were significantly increased and decreased, respectively, after treatment with high concentrations of BPA and its analogues. BPA, BPS and BPF may also impair melanocyte function and pose a health hazard.
In addition, recent studies on environmental and occupational exposure to bisphenol compounds in Finland have reported higher levels of BPA and BPF in non-occupationally exposed persons than the corresponding levels reported in the recent literature. Concentrations of BPA and BPF in workers' urine samples were in the same range as the corresponding concentrations in the non-occupationally exposed population. Exposure to BADGE and BFDGE may occur during sewer line replacement and floor coating work.These results reconfirm that dermal contamination accounts for a proportion of the total exposure. Although measured urine levels indicate that absorption of these bisphenol compounds is unlikely to pose a systemic health hazard, the risk of skin sensitisation remains.
References:
[1] J. APAU E A Akwasi Acheampong. Exposure to bisphenol A, bisphenol F, and bisphenol S can result in obesity in human body[J]. Cogent Chemistry, 2018. DOI:10.1080/23312009.2018.1506601.
[2] MINGQUAN HUANG . Bisphenol A and its analogues bisphenol S, bisphenol F and bisphenol AF induce oxidative stress and biomacromolecular damage in human granulosa KGN cells[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 253. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126707.
[3] GOENKA S. Disruption of functions of primary human neonatal melanocytes cultured in the presence of bisphenol A and its analogs bisphenol F and bisphenol S[J]. Journal of hazardous materials letters, 2024, 5. DOI:10.1016/j.hazl.2024.100110.
[4] SIMO P. PORRAS. Environmental and occupational exposure to bisphenol compounds in Finland[J]. Toxicology letters, 2024, 398: 1-. DOI:10.1016/j.toxlet.2024.06.001.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Biological implications of Bisphenol A Jun 23, 2022
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical produced in large quantities for use primarily in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins.
- What Is Bisphenol A and Why Is It Bad for You? Feb 18, 2022
Bisphenol A is a diphenylmethane derivative with two hydroxyphenyl groups. Bisphenol A (BISPHENOL A) is a colorless solid that is used in the synthesis of commercial plastics, including polycarbonates
- Uses of Bisphenol A Nov 26, 2021
Bisphenol A (BPA) was first synthesized in 1891, but it was not used widely until applications in the plastic industry were identified the 1950s. One method of production is by the condensation of 2 mol of phenol with 1 mol of acetone while
L(+)-Lactic acid, also known as milk acid occurs naturally in several foods and is primarily found in fermented milk products, such as: sour milk, cheese, buttermilk and yogurt.....
Jan 24,2025Biochemical EngineeringDesloratadine is a biologically active metabolite of the second-generation antihistamine loratadine. It is a highly selective peripheral H1 receptor antagonist and belongs to the antihistamine group of drugs.....
Dec 16,2024APIBisphenol A
80-05-7You may like
- Bisphenol A BPA
-

- $200.00 / 1kg
- 2025-01-24
- CAS:80-05-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20ton
- Bisphenol A
-

- $999.00/ ton
- 2025-01-23
- CAS:80-05-7
- Min. Order: 1ton
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5000
- Bisphenol A
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2025-01-22
- CAS:80-05-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000KG/Month