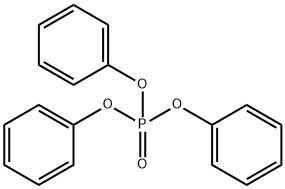
Preparation method of triphenyl phosphate
Aug 16,2022
Triphenyl phosphate (TPHP) is primarily used as either a flame retardant or plasticizer, and is listed as an ingredient in nail polishes[1]. Triphenyl phosphate (TPhP), a typical organophosphate ester, is frequently detected in the environment and biota samples. It has been implicated as a neurotoxin as its structure is similar to neurotoxic organophosphate pesticides.

Picture 1 Triphenyl phosphate
Developmental neurotoxicity of triphenyl phosphate in zebrafish larvae
TPhP exposure significantly altered the content of the neurotransmitters γ-aminobutyric and histamine. Downregulation of the genes related to central nervous system development (e.g., α1-tubulin, mbp, syn2a, shha, and elavl3) as well as the corresponding proteins (e.g., α1-tubulin, mbp, and syn2a) was observed, but the gap-43 protein was found to upregulated. Finally, marked inhibition of total acetylcholinesterase activity, which is considered as a biomarker of neurotoxicant exposure, was also observed in the larvae. Our results indicate that exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of TPhP can affect different parameters related to center nervous system development, and thus contribute to developmental neurotoxicity in early developing zebrafish larvae.[1]
Preparation method of triphenyl phosphate
The invention provides a preparation method of triphenyl phosphate. Firstly, phenol is added to an organic solvent, phosphorus oxychloride is added in a dropwise mode, meanwhile, a metal catalyst is added, and after a heat preservation reaction, triphenyl phosphate is obtained through after-treatment. The preparation method is simple in process step, high in product yield and low in production energy consumption, three-waste emission is greatly reduced, production cost is reduced, the product purity is high, the impurity content is low, and the yield is high[2].
Method for preparing triphenyl phosphate
The invention discloses a method for preparing triphenyl phosphate through phenol extraction in aryl phosphoric ester production waste water[3]. The method comprises the following steps of adding acid into the aryl phosphoric ester alkali washing waste water for regulating the pH value to 6 to 7; stirring and still standing layering to obtain an oil layer and waste water with the phenol content beinglower than 25000 ppm; adding triphenyl phosphate extraction agents into the waste water for stirring extraction; transferring an extraction phase into a distillation kettle for reduced pressure distillation dewatering; putting the dewatered extracts into an esterification kettle; next, adding phosphorus oxychloride and anhydrous magnesium chloride for esterification reaction to obtain triphenyl phosphate coarse products; sequentially performing acid washing, alkali washing, water washing and distillation treatment to finally obtain the qualified triphenyl phosphate finished product. Through the unified use of the triphenyl phosphate with the most simple phenol reuse process and least links as the extraction agents, one set of equipment can be used for solving the phenol recovery problem of various aryl phosphoric ester waste water in a concentrated way.
Triphenyl phosphate recycling method
The invention belongs to the technical field of cefaclor waste treatment, and particularly relates to a triphenyl phosphate recycling method. The method includes following steps: step 1, preparing recycling raw materials; step 2, soaking the recycling raw materials in water for certain time to enable water-soluble substances in the recycling raw materials to be dissolved fully; step 3, removing moisture in the recycling raw materials by means of centrifuging, and drying to obtain a crude product-triphenyl phosphate; step 4, adding the crude product-triphenyl phosphate, methanol and activated carbon into a decoloring pot, and treating for several times to obtain triphenyl phosphate. A physical method is adopted to water-wash, re-crystallize and purify triphenyl phosphate solid waste to obtain triphenyl phosphate crystals. By the method, recycling cost is lowered greatly, the waste is turned into things of value, and environment resources are saved.
Reference
1 Shi Q, Wang M, Shi F, et al. Developmental neurotoxicity of triphenyl phosphate in zebrafish larvae[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2018, 203: 80-87.
2 GENG YUNHUA, CN105254666A;CN105254666B.
3 WANG YI; LYU YUNXING; FANG JIAN; WANG HAIHANG. CN109535199A;CN109535199B
4 CHI ZHENGWEI,CN107236000A;CN107236000B
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Triphenyl Phosphate: Applications and its Reproductive Toxicity Oct 22, 2024
Triphenyl phosphate enhances fire safety in consumer goods but poses reproductive toxicity concerns, necessitating stringent regulations for ecological and health protection.
Triphenyl phosphate
115-86-6You may like
Triphenyl phosphate manufacturers
- Triphenyl phosphate
-

- $10.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-30
- CAS:115-86-6
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20 ton
- Triphenyl phosphate
-

- $10.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-23
- CAS:115-86-6
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100 mt
- Triphenyl phosphate
-
- $0.00 / 200kg
- 2025-04-15
- CAS:115-86-6
- Min. Order: 20kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20 tons