| 60% |
With KF;palladium diacetate; In tetrahydrofuran; |
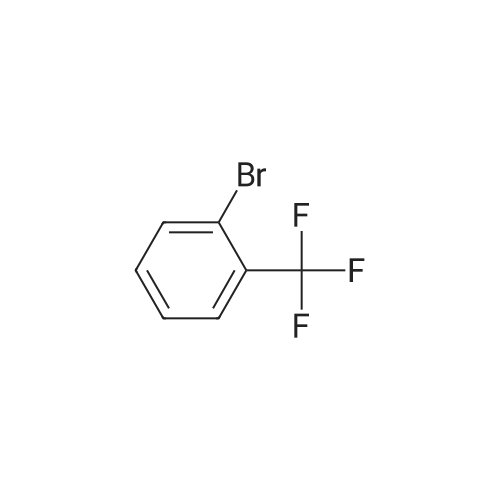
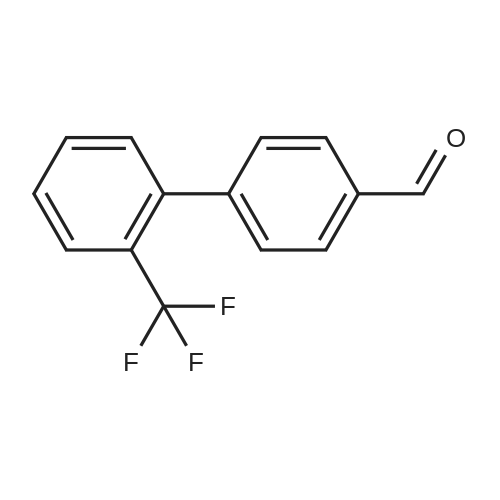
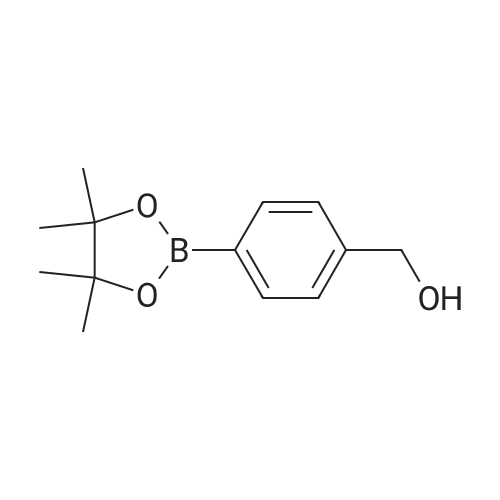
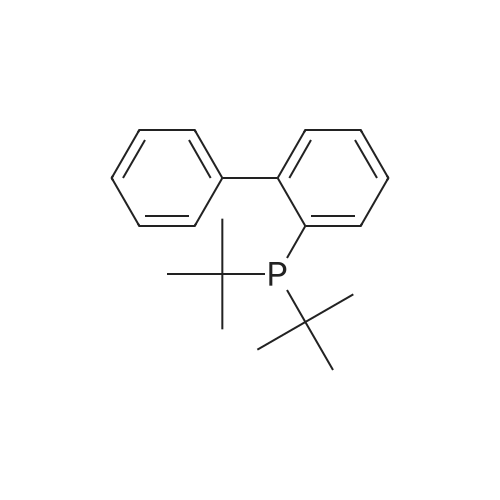
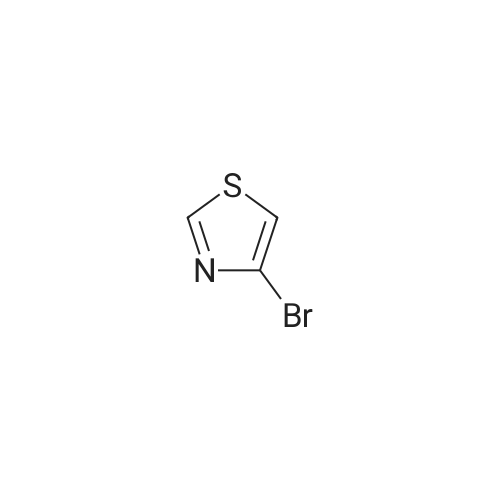
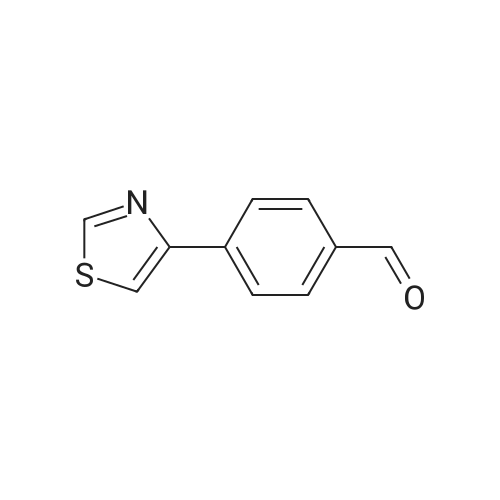
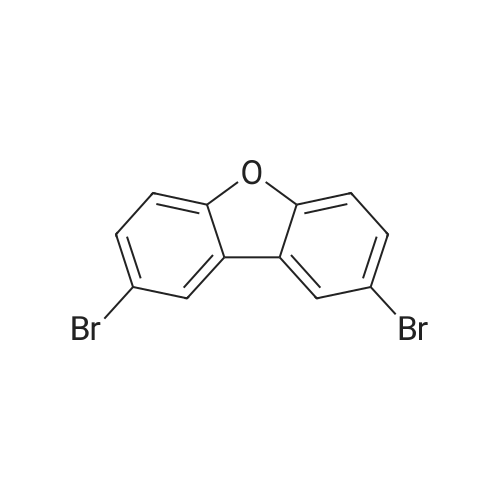
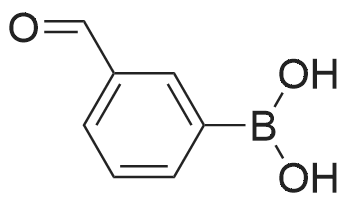
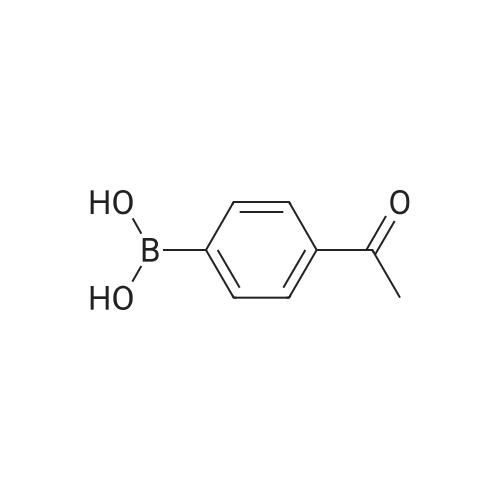
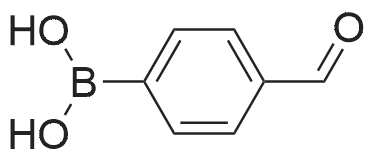
(4'-Formylbiphenyl-3-ylmethyl)-carbamic acid 9H-fluoren-9-ylmethyl ester (S30). 4-Formylphenylboronic acid (5.0 g, 33 mmol), aryl bromide S27 (9.0 g, 22 mmol), KF (3.8 g, 66 mmol), <strong>[224311-51-7]biphenyl-2-yl-di-tert-butyl-phosphane</strong> (0.26 g, 0.88 mmol), and palladium(II) acetate (0.099 g, 0.44 mmol) were charged into an oven-dried flask. After one evacuation/backfill cycle with Ar, the solids were dissolved in THF (45 mL) and heated to reflux with stirring. After 5 h, the reaction was diluted with ethyl acetate, filtered through a celite pad and washed with 1 M NaOH. The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate and the combined organics were then washed with brine, dried over MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo to afford an orange oil (13 g). The crude oil was purified by flash column chromatography (silica gel, 30percent ethyl acetate/hexanes) to obtain aldehyde S29 as a yellow oil (5.7 g, 60percent). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): delta10.06 (s, 1H), 7.95 (d, 2H, J=8.2 Hz), 7.76 (d, 2H, J=7.5 Hz), 7.74 (d, 2H, J=8.2 Hz), 7.59 (d, 2H, J=7.5 Hz), 7.56 (m, 1H), 7.55 (s, 1H), 7.46 (dd, 1H, J=7.9 Hz, 7.9 Hz), 7.39 (dd, 2H, J=7.5 Hz, 7.5 Hz), 7.33 (m, 1H), 7.29 (dd, 2H, J=7.5 Hz, 7.5 Hz), 5.16 (broad s, 1H), 4.48 (d, 2H, J=7.0 Hz), 4.47 (s, 2H), 4.24 (t, 1H, J=7.0 Hz). ESI/MS: 456 (M+Na+). |
| 60% |
With KF;palladium diacetate; In tetrahydrofuran; |
(4'-Formylbiphenyl-3-ylmethyl)-carbamic acid 9H-fluoren-9-ylmethyl ester (S30). 4-Formylphenylboronic acid (5.0 g, 33 mmol), aryl bromide S27 (9.0 g, 22 mmol), KF (3.8 g, 66 mmol), <strong>[224311-51-7]biphenyl-2-yl-di-tert-butyl-phosphane</strong> (0.26 g, 0.88 mmol), and palladium(II) acetate (0.099 g, 0.44 mmol) were charged into an oven-dried flask. After one evacuation/backfill cycle with Ar, the solids were dissolved in THF (45 mL) and heated to reflux with stirring. After 5 h, the reaction was diluted with ethyl acetate, filtered through a celite pad and washed with 1 M NaOH. The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate and the combined organics were then washed with brine, dried over MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo to afford an orange oil (13 g). The crude oil was purified by flash column chromatography (silica gel, 30percent ethyl acetate/hexanes) to obtain aldehyde S29 as a yellow oil (5.7 g, 60percent). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): delta10.06 (s, 1H), 7.95 (d, 2H, J=8.2 Hz), 7.76 (d, 2H, J=7.5 Hz), 7.74 (d, 2H, J=8.2 Hz), 7.59 (d, 2H, J=7.5 Hz), 7.56 (m, 1H), 7.55 (s, 1H), 7.46 (dd, 1H, J=7.9 Hz, 7.9 Hz), 7.39 (dd, 2H, J=7.5 Hz, 7.5 Hz), 7.33 (m, 1H), 7.29 (dd, 2H, J=7.5 Hz, 7.5 Hz), 5.16 (broad s, 1H), 4.48 (d, 2H, J=7.0 Hz), 4.47 (s, 2H), 4.24 (t, 1H, J=7.0 Hz). ESI/MS: 456 (M+Na+). |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping